In today’s digital economy, data is the new oil, but managing it efficiently is the key to unlocking its value. Businesses are increasingly dealing with massive amounts of diverse data from web traffic, IoT devices, social media, transactions, and more. Traditional data warehouses struggle with the volume, variety, and velocity of modern data. Data lakes emerged to store raw, unstructured data cost-effectively, but they often fell short in governance, performance, and analytics capabilities. Enter the Data Lakehouse: a unified data architecture combining the best of data lakes and data warehouses.
In this post, we’ll unpack what a data lakehouse is, why it matters, how it works, and what it means for organizations aiming to build a scalable, modern data platform.
What is a Data Lakehouse?
A data lakehouse is an architectural paradigm that merges the flexibility and low-cost storage of a data lake with the management features and performance optimizations of a data warehouse. Unlike a traditional data lake that stores data in its raw form with minimal structure, or a warehouse that imposes rigid schemas upfront, a lakehouse provides a middle ground: it allows storing raw and structured data in open formats, but with features like ACID transactions, governance, and performance optimizations.
The term “lakehouse” was popularized by Databricks but has since gained industry-wide traction. Lakehouses sit on top of cloud object storage (e.g., Amazon S3, Azure Data Lake Storage, or Google Cloud Storage), and introduce technologies like Delta Lake, Apache Iceberg, or Apache Hudi to manage data reliably.
Why Traditional Architectures Fall Short
Before lakehouses, organizations often had to choose between two extremes:
- Data Warehouses: Optimized for structured data, high-performance SQL queries, and BI dashboards. But they’re expensive for large volumes of raw or semi-structured data, and schema changes can be rigid.
- Data Lakes: Affordable, scalable storage for raw data. They support diverse data types and ingestion speeds but lack built-in data management, data quality enforcement, transactional updates, and fast analytics.
This led to the “Lambda architecture” or “two-tier architecture,” where businesses maintained both a data lake for storage and exploration, and a warehouse for analytics and reporting. The result? Data duplication, complex ETL pipelines, stale data, and high maintenance costs.
Key Features of a Data Lakehouse
Data lakehouses aim to unify these separate worlds. Here’s how they do it:
- Unified Storage: All data—structured, semi-structured, and unstructured—resides in a single storage system.
- ACID Transactions: Using table formats like Delta Lake or Apache Iceberg, lakehouses support transactions on large-scale datasets, ensuring data consistency and reliability during updates or merges.
- Schema Enforcement & Evolution: Lakehouses allow enforcing schemas (avoiding the “data swamp” problem) while also supporting schema evolution for flexible data ingestion.
- Time Travel: Users can query historical versions of data tables, enabling debugging, auditing, and rollback.
- Performance Optimizations: Techniques like data skipping, column pruning, and file compaction improve query performance dramatically, making lakehouses suitable for both batch and interactive analytics.
- Open Data Formats: Lakehouses use open-source table formats (Parquet, ORC) instead of proprietary storage, avoiding vendor lock-in.
- Governance and Security: Fine-grained access controls, data masking, and audit logs allow enterprises to meet compliance and security requirements.
Benefits of the Lakehouse Architecture
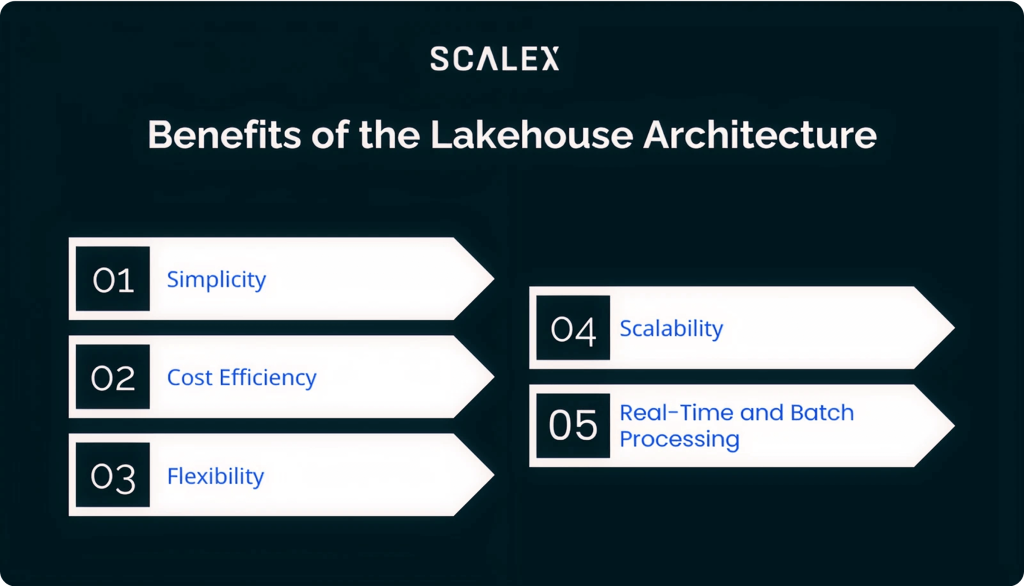
Organizations adopting a lakehouse architecture unlock several benefits:
- Simplicity: One platform for all analytics use cases—BI, SQL, machine learning—reduces data silos and simplifies data pipelines.
- Cost Efficiency: Using inexpensive cloud object storage reduces storage costs compared to data warehouses.
- Flexibility: Data scientists, analysts, and engineers can work directly on raw data in open formats, while still benefiting from structured table management.
- Scalability: Cloud-native lakehouses can elastically scale to petabytes of data, handling growing data volumes seamlessly.
- Real-Time and Batch Processing: Lakehouses support both streaming and batch data ingestion, enabling modern use cases like fraud detection or predictive maintenance.
How Does a Data Lakehouse Work?
A typical data lakehouse architecture consists of several components working together:
- Storage Layer: Cloud object storage stores the data in open file formats.
- Table Format Layer: Technologies like Delta Lake, Iceberg, or Hudi organize the data files into transactional tables with metadata (schema, partitions, statistics).
- Processing Engines: Engines like Apache Spark, Trino, Dremio, or Presto run queries against the lakehouse tables with support for both batch and interactive workloads.
- Metadata and Catalog: Systems like AWS Glue, Unity Catalog, or Hive Metastore track datasets, schemas, and permissions.
- Ingestion & ETL: Tools like Apache NiFi, dbt, or custom pipelines bring data into the lakehouse from multiple sources.
- Consumption Layer: BI tools (e.g., Tableau, Power BI), notebooks, and ML frameworks connect directly to the lakehouse tables for analytics and model training.
Common Use Cases for Data Lakehouses
- Business Intelligence: Analysts can build dashboards directly on top of lakehouse tables using SQL.
- Data Science & ML: Data scientists can experiment on full-fidelity data without having to move it elsewhere.
- Streaming Analytics: Combine real-time and historical data for applications like anomaly detection or customer personalization.
- Data Sharing: Securely share data with partners using open formats, reducing friction compared to traditional data warehouses.
- Data Governance & Compliance: Centralized data access policies and auditability ensure organizations meet regulations like GDPR or HIPAA.
Challenges and Considerations
While promising, lakehouses are not silver bullets. Some challenges include:
- Complexity of Implementation: Moving to a lakehouse requires redesigning pipelines and workflows.
- Query Performance Parity: While lakehouse engines have improved massively, very high-performance workloads might still perform better in specialized warehouses.
- Data Management Discipline: Without proper governance, a lakehouse can devolve into an unmanaged data swamp.
The Future of Data Architectures
Data lakehouses are rapidly becoming the de facto architecture for organizations seeking flexibility, scalability, and unified analytics capabilities. Vendors like Databricks, Snowflake (with Unistore), AWS (with Amazon Lake Formation), and Google Cloud are investing heavily in lakehouse capabilities. The emergence of open table formats is democratizing lakehouse adoption beyond proprietary stacks.
As businesses collect ever-larger and more diverse datasets, the ability to efficiently store, process, and analyze all data in one platform is a game changer. The lakehouse architecture empowers companies to break down silos, democratize data access, and build data-driven products faster.
Conclusion
The data lakehouse represents a major evolution in modern data architectures—one that blends the scalability of data lakes with the reliability and performance of warehouses. By unifying disparate data platforms into a single source of truth, lakehouses enable organizations to innovate at scale, reduce costs, and simplify operations.
In the coming years, expect lakehouses to become the cornerstone of data strategies across industries. Organizations that embrace this architecture will be better positioned to harness the full potential of their data, deliver insights faster, and stay competitive in an increasingly data-driven world.