As generative AI becomes increasingly embedded in business operations, customer experiences, and creative processes, its potential for transforming industries is clearer than ever. From generating text and code to creating images, videos, and even music, generative AI offers a leap forward in automation and productivity. However, with great power comes great responsibility — and risk. These systems are only as reliable as the data they learn from and the rules governing their use. Enter data governance — the unsung hero of AI stability, compliance, and ethics.
In this post, we’ll explore how robust data governance frameworks serve as a critical safeguard against generative AI failures, ensuring that innovation is both responsible and sustainable.
What Is Data Governance?
Data governance is the set of policies, processes, and standards that ensure data is accurate, consistent, secure, and used responsibly across an organization. It defines who can take what actions with what data, and under what circumstances. Effective governance involves data quality management, metadata standards, access controls, regulatory compliance, and lifecycle management.
In the context of AI, data governance doesn’t just manage data — it shapes how machines learn, operate, and evolve. Without it, generative AI is at risk of failure across technical, ethical, legal, and reputational fronts.
Common Generative AI Failures
Before diving into how data governance prevents issues, let’s understand what can go wrong with generative AI:
- Hallucinations – AI generates plausible-sounding but false or misleading content.
- Bias and Discrimination – AI reflects and amplifies social, racial, or gender biases in the training data.
- IP Infringement – Outputs that replicate copyrighted content or proprietary data.
- Security Breaches – Sensitive information is leaked due to poor data handling or model behavior.
- Compliance Violations – Use of personal data without consent breaches laws like GDPR, HIPAA, or CCPA.
- Model Drift – Performance degradation over time due to outdated or irrelevant data inputs.
- Misinformation Spread – AI used to create fake news, deepfakes, or manipulative content.
Each of these failures is directly or indirectly a result of poor data practices — the precise problem that data governance is designed to solve.
How Data Governance Prevents These Failures
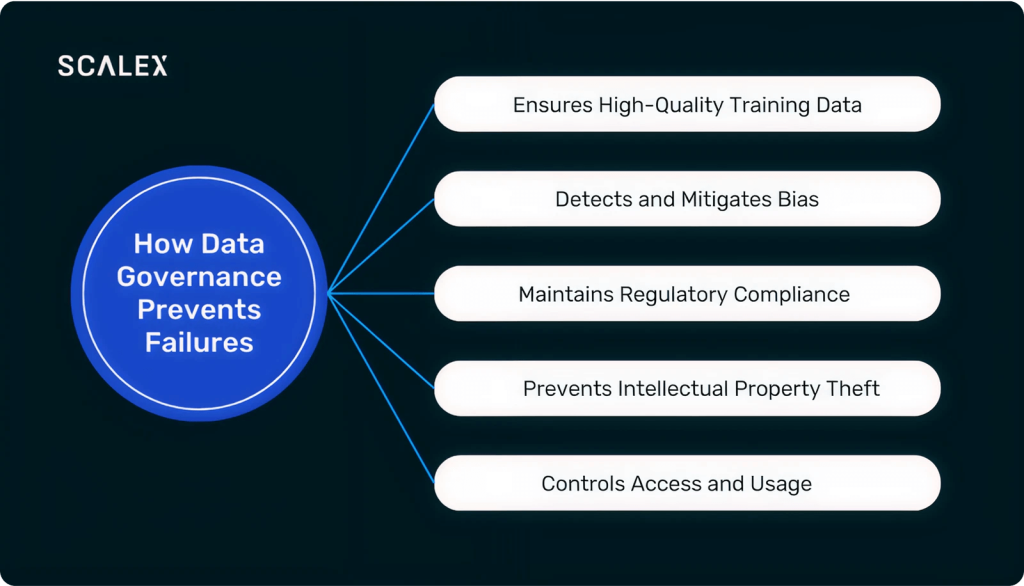
1. Ensures High-Quality Training Data
Generative AI models are only as good as the data they’re trained on. Poor quality data can lead to incoherent outputs, hallucinations, or flawed logic. Data governance enforces standards for:
- Data accuracy and consistency
- Source validation and lineage tracking
- Deduplication and noise reduction
This minimizes the risk of garbage-in, garbage-out scenarios and ensures that models learn from reliable sources.
2. Detects and Mitigates Bias
Bias in AI is a critical ethical and operational concern. Data governance frameworks include mechanisms to audit and measure bias in datasets, apply fairness metrics, and set policies for inclusion.
For example:
- Mandating demographic balance in training sets
- Using bias detection tools during preprocessing
- Engaging cross-functional review teams (legal, DEI, ethics)
These steps help prevent biased outputs that could alienate customers, violate anti-discrimination laws, or tarnish brand reputation.
3. Maintains Regulatory Compliance
Whether it’s GDPR in Europe, CCPA in California, or HIPAA for healthcare, modern organizations must respect strict data privacy laws. A mature data governance program provides:
- Data classification and labeling
- Consent and purpose management
- Data minimization and retention policies
- Right-to-be-forgotten workflows
Without governance, generative AI systems may inadvertently generate outputs containing personal data or operate on datasets collected illegally — leading to lawsuits and fines.
4. Prevents Intellectual Property Theft
Generative models trained on copyrighted material can unintentionally reproduce it, exposing organizations to intellectual property disputes. Governance ensures:
- Proper licensing of training data
- Exclusion of proprietary or sensitive datasets
- Documentation of dataset provenance
- Model behavior audits to detect replication
By maintaining rigorous oversight of data sources and training processes, organizations can respect copyright laws and industry norms.
5. Controls Access and Usage
One of the most effective ways to reduce AI risk is to control who can access what data and models. Data governance tools implement:
- Role-based access control (RBAC)
- Audit trails for usage tracking
- Approval workflows for dataset/model deployment
- Encryption and masking of sensitive attributes
These controls prevent misuse, insider threats, and unauthorized access to training data or model internals.
The Role of Governance Tools and Teams
Implementing data governance is not just about policies — it requires technology and people. Organizations often establish Data Governance Councils that include stakeholders from IT, legal, compliance, data science, and business units.
Popular tools include:
- Data catalogs (e.g., Collibra, Alation) for metadata management
- Data quality tools (e.g., Informatica, Talend) for cleansing and validation
- Data quality tools (e.g., Informatica, Talend) for cleansing and validation
These systems help institutionalize governance as an ongoing practice, not a one-off audit.
A Real-World Example: Financial Services
Consider a bank using generative AI to generate customer investment reports. Without proper governance, the model might:
- Fabricate financial data (hallucination)
- Favor products based on biased data
- Leak customer details in a generated report
With governance in place:
- Only verified, real-time financial data is used
- Models are audited for fairness and compliance
- Sensitive information is masked or omitted
- Human reviewers validate outputs before distribution
The result? A safer, more reliable, and customer-trusted application of generative AI.
Conclusion: Governance Is the Foundation of Responsible AI
Generative AI can unlock enormous value — but only if it’s built on a foundation of trusted data and ethical practices. Data governance is not a bureaucratic hurdle; it’s a strategic necessity.
By implementing robust governance frameworks, organizations can:
- Improve AI reliability and performance
- Ensure legal and ethical compliance
- Build trust with customers and stakeholders
- Reduce reputational and financial risk
As generative AI continues to evolve, the organizations that invest in strong data governance today will be the ones leading tomorrow’s innovation — safely, responsibly, and sustainably.